What is Costochondritis and How to Treat It?
What is Costochondritis?
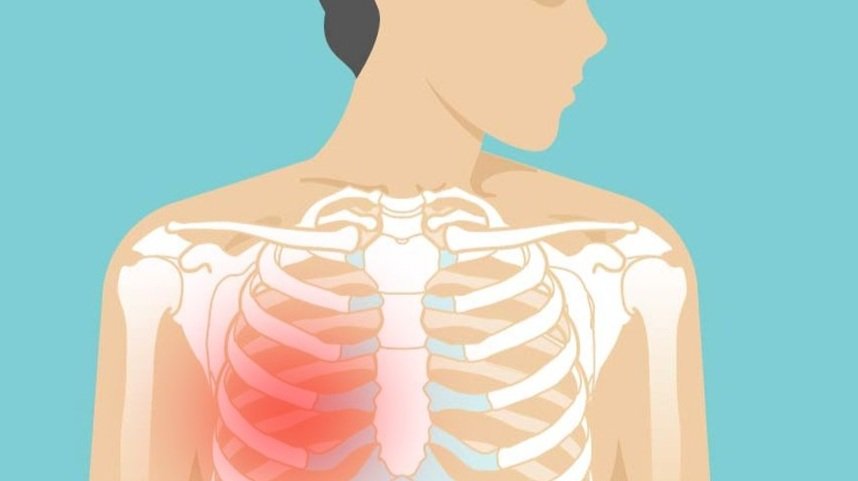
Costochondritis, sometimes referred to as chest wall pain, costosternal syndrome, or costosternal chondrodynia, is an inflammatory condition of the cartilage where the upper ribs attach to the sternum. This area is called the costosternal junction.
Since the symptoms of costochondritis can mimic those of a heart attack, the pain it causes is often worrisome. However, unlike heart-related pain, costochondritis does not involve the heart and is rarely dangerous.
What Causes Costochondritis?
The exact cause of costochondritis is not always clear, but several factors can lead to inflammation in the costosternal junction:
Injury or Trauma: Physical trauma from falls, car accidents, or sports injuries can cause inflammation in the chest wall.
Repetitive Strain: Activities that place repetitive stress on the chest, such as heavy lifting or intense exercise, can trigger costochondritis.
Infection: Rarely, infections caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi can inflame the cartilage in the chest.
Arthritis: People with certain types of arthritis, like ankylosing spondylitis or rheumatoid arthritis, may be more susceptible to developing costochondritis.
Surgical Procedures: Chest or upper-abdominal surgeries can sometimes lead to costochondritis as the body heals from incisions or trauma.
Symptoms of Costochondritis
Costochondritis primarily manifests as a sharp or aching pain in the chest, often on the left side but sometimes on both sides. Here are the common symptoms:
Localized Chest Pain: Pain typically occurs where the ribs meet the sternum, particularly around the second to fifth ribs.
Tenderness: Pressing on the affected area can often reproduce the pain.
Pain that Worsens with Movement: Certain activities, like deep breathing, coughing, or physical exercise, may aggravate the pain.
Radiating Pain: Occasionally, pain may spread to the back, shoulders, or abdomen, which can be mistaken for a heart-related issue.
How to Diagnose Costochondritis
Because costochondritis shares symptoms with other more severe conditions, it’s essential to see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis. Doctors often perform a physical examination, checking for tenderness in the chest area and ruling out other causes of chest pain through diagnostic tests, such as:
Electrocardiogram (EKG): To rule out heart-related causes.
X-rays or CT Scans: To check for fractures or lung issues.
Blood Tests: To detect signs of infection or inflammation.
Treatment for Costochondritis
Costochondritis often resolves on its own with minimal treatment, but several methods can help alleviate pain and speed up recovery. Here are the most effective treatments for managing costochondritis:
1. Rest and Activity Modification
Giving your body a break from strenuous activities is key to reducing inflammation. Avoid activities that trigger or worsen the pain, especially exercises that involve the upper body.
2. Hot and Cold Therapy
Alternating between hot and cold packs can help reduce inflammation and ease pain. Applying an ice pack for 10-15 minutes can reduce swelling, while a warm compress can relax tight muscles around the chest area.
3. Pain Relievers and Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can effectively reduce pain and inflammation associated with costochondritis. Acetaminophen is also an option, though it lacks anti-inflammatory effects.
Note: Always follow recommended doses and consult your doctor before starting any medication, especially if you have other health conditions.
4. Physical Therapy
A physical therapist can guide you through gentle stretching and strengthening exercises to improve mobility and relieve tension in the chest area. Physical therapy can be particularly helpful for those whose costochondritis is linked to muscle strain or posture issues.
5. Posture Improvement
Poor posture can strain the muscles and ligaments in the chest, leading to or worsening costochondritis. Focus on maintaining an upright posture with shoulders relaxed and back. Simple postural exercises, like shoulder blade squeezes, can help.
6. Alternative Therapies
Some individuals find relief from alternative treatments, such as massage therapy. While these therapies are not a primary treatment, they can complement other methods by reducing muscle tension and enhancing relaxation.
How Long Does It Take to Recover from Costochondritis?
The recovery time for costochondritis varies. For many people, the pain resolves within a few days to weeks with proper rest and care. However, in some cases, it can last several months, especially if the inflammation is severe or if the condition is triggered by chronic strain. Following the recommended treatment plan and avoiding activities that stress the chest area can help expedite recovery.
When to See a Doctor
Although costochondritis is typically harmless, it’s essential to seek medical attention if you experience any of the following symptoms:
Sudden, severe chest pain that does not improve with rest
Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
Pain that radiates to the left arm, jaw, or back
Fever or other signs of infection
These symptoms may indicate a more serious condition, such as a heart attack or an infection, and require immediate medical evaluation.